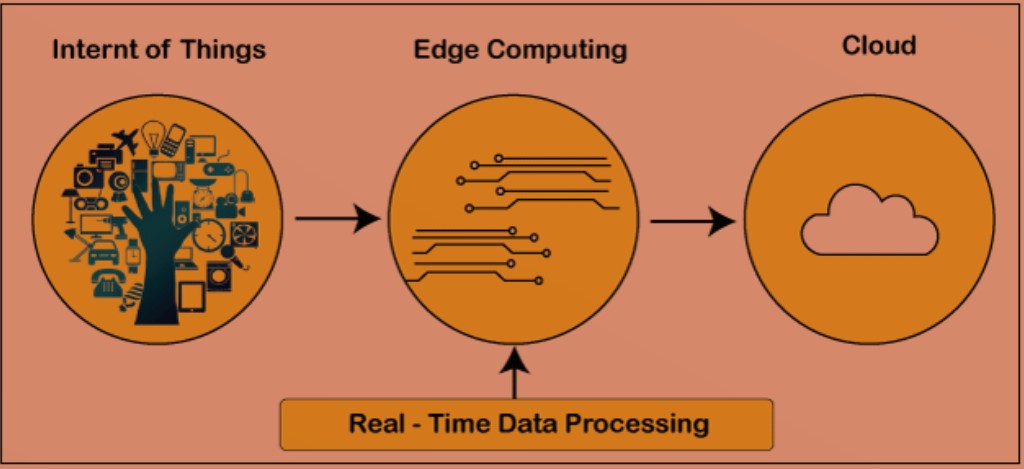
Edge computing and cloud computing are two different approaches to managing data and processing information. Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, while cloud computing involves storing and processing data in centralized data centers.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.
What is edge computing?
Edge computing is a type of computing that brings data storage and computation closer to the users and devices that need it, rather than relying on centralized servers. Edge computing can be used to improve the performance of applications and services by reducing latency and increasing security. Additionally, edge computing can help organizations save on bandwidth and infrastructure costs. Edge computing is particularly well suited for applications that require real-time responses, such as video streaming, virtual reality, and gaming. Additionally, edge computing can be used to process data from sensors and devices in the Internet of Things (IoT).
Comparing Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing
Here are some differences of edge computing and cloud computing,
1. Edge computing is typically used for tasks that require real-time or near-real-time processing, while cloud computing can be used for tasks that can tolerate some latency.
2. Edge computing can be used to offload compute-intensive tasks from the cloud, reducing overall bandwidth and latency requirements.
3. Cloud computing generally requires more upfront investment in infrastructure and personnel, while edge computing can be deployed more quickly and with less investment.
4. Edge computing can be more reliable than cloud computing, since there is no single point of failure.
5. Edge computing can be more secure than cloud computing, since data is not transmitted over the internet and is instead stored locally.
6. Edge computing can be more energy-efficient than cloud computing, since data does not need to be transmitted long distances.
7. Edge computing can be used to improve the performance of applications that require low latency, such as augmented reality and virtual reality.
8. Edge computing can be used to process data from sensors and other devices in real-time, allowing for faster reaction times to changes in the environment.
9. Edge computing can be used in situations where internet connectivity is limited or unavailable, such as in rural areas or during a power outage.
10. Edge computing can provide a more personalized experience for users since data is processed and stored locally rather than in a centralized location.
Conclusion Edge computing and cloud computing are two very different ways of handling data. It’s important to understand the benefits and drawbacks of each before making a decision about which is right for your organization. We hope this article has helped you better understand edge computing and cloud computing, their differences, and how to choose the best option for your needs. Wave Internet is one of the most reliable and affordable ways to get cloud computing services. It offers high speed internet service that is perfect for businesses that require fast and reliable access to their data. wave internet also provides a variety of other services such as Wave phone service or wave tv cable.